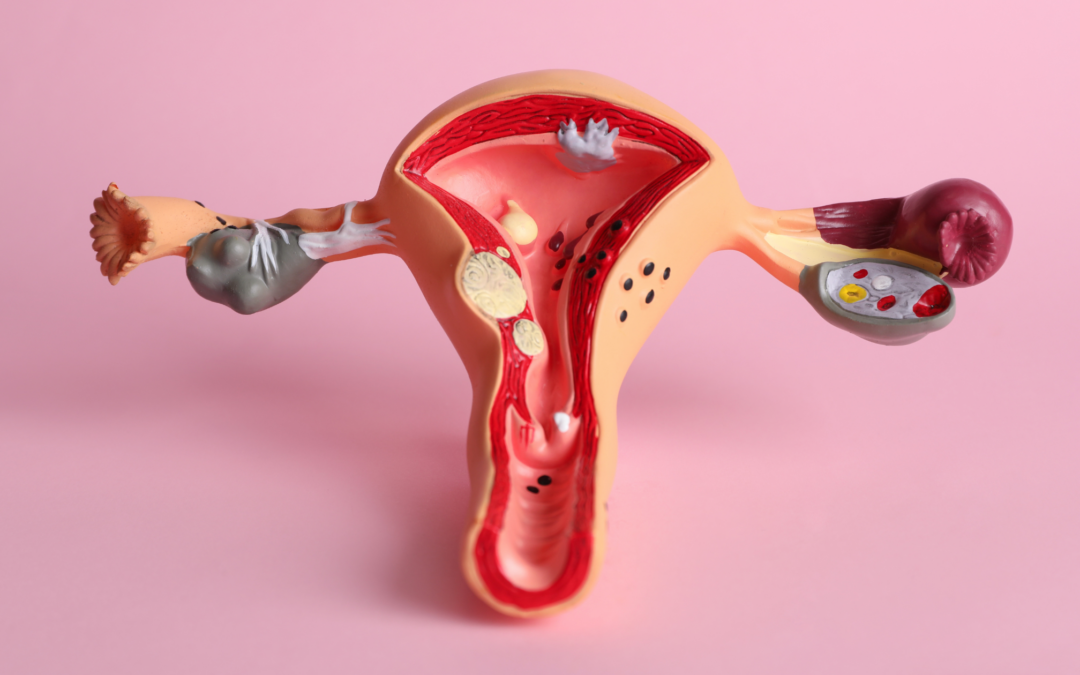
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, commonly on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic peritoneum. This tissue responds to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, leading to inflammation, scarring, and the formation of adhesions.
What Causes Endometriosis?
The frustrating part is that there is no known exact cause. The best guesses are that it is due to several factors, such as genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and immune dysfunction, which may contribute to its development.
What are the Symptoms?
Symptoms of endometriosis vary widely among individuals but commonly include:
-
- Pelvic pain: Chronic pelvic pain, worse during menstruation, is a hallmark symptom of endometriosis. This pain radiates to the lower back and legs, impacting daily activities and quality of life.
- Menstrual irregularities: Women experience heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, as well as clotting and spotting between periods.
- Pain during intercourse: Dyspareunia, or pain during sexual intercourse, is another common symptom. This often occurs deep within the pelvis.
- Infertility: Endometriosis affects fertility by interfering with ovulation, fertilization, and implantation of the embryo. Up to 30-50% of women with endometriosis may experience infertility.
How is it Diagnosed?
Diagnosing endometriosis is challenging due to the variability of symptoms and the lack of definitive diagnostic tests. However, healthcare providers utilize a combination of medical history, pelvic exams, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or MRI), and laparoscopy (a minimally invasive surgical procedure) to confirm the presence of endometrial implants.
How is it Treated?
Treatment options aim to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life. Conventional approaches include:
-
- Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and hormonal therapies (such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists) help alleviate pelvic pain and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic excision or ablation of endometrial tissue is often recommended for individuals with severe symptoms or fertility concerns. In some cases, hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries) is considered.
- Fertility treatments: Assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be pursued by individuals struggling with infertility due to endometriosis.
Integrative Approaches to Managing Endometriosis:
In addition to conventional treatments, integrative approaches focusing on lifestyle modifications, nutrition, and holistic therapies play a valuable role in managing endometriosis and promoting overall well-being. Here are some strategies supported by evidence and endorsed by reputable organizations:
-
- Health Coaching: Health coaches provide personalized support and guidance to individuals with endometriosis, helping them navigate treatment options, adopt healthy lifestyle habits, and cope with emotional challenges. Health coaching complements conventional care and improves treatment outcomes by addressing stress management, sleep hygiene, and physical activity.
- Nutrition and Dietary Modifications: Emerging research suggests that diet will influence the development and progression of endometriosis. While more studies are needed, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids will help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Foods to consider incorporating into the diet include leafy greens, berries, fatty fish, flaxseeds, and turmeric. Additionally, limiting the consumption of processed foods, red meat, dairy, and caffeine benefits some individuals.
- Mind-Body Therapies: Mindfulness-based practices, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, help manage pain, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being in individuals with endometriosis. These mind-body therapies promote relaxation, enhance resilience, and empower individuals to participate actively in their healing journey.
- Herbal Remedies and Supplements: Certain herbs and supplements show promise in alleviating symptoms associated with endometriosis. For example, herbal formulations containing ingredients like chasteberry (Vitex agnus-castus), turmeric, and ginger help regulate hormonal balance and reduce inflammation. Additionally, supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and vitamin D benefit individuals with endometriosis.
Conclusion:
Endometriosis is a complex and multifaceted condition requiring a comprehensive management approach. By integrating conventional treatments with evidence-based strategies such as health coaching, nutrition, and holistic therapies, individuals with endometriosis will enhance their quality of life, reduce symptoms, and promote overall wellness. At Integrative Family Medicine of Asheville, we are committed to providing compassionate care and personalized support to individuals with endometriosis, empowering them to thrive on their healing journey. If you or a loved one are struggling with endometriosis, reach out to our team to learn more about our integrative approach and how we can assist you on your path to wellness.
This blog post was written by Sarah Schopbach, FNP for Integrative Family Medicine of Asheville.
Helpful Links: